The GPA scale is a standardized system used by educational institutions to measure a student’s academic performance. GPA stands for Grade Point Average, and it is calculated by assigning numerical values to letter grades and then averaging them. This system provides a clear, concise way for schools, colleges, and employers to assess a student’s academic achievements. Understanding the GPA scale is crucial for students, as it affects college admissions, scholarship eligibility, and even career opportunities.
Table of Contents
How the GPA Scale Works
The most commonly used GPA Scale in the United States is the 4.0 scale. On this scale, an “A” grade typically equates to 4.0 points, a “B” is 3.0, a “C” is 2.0, a “D” is 1.0, and an “F” is 0. These points are then multiplied by the number of credits for each course, summed up, and divided by the total number of credits to determine the overall GPA. Some schools also use weighted GPA scales, which take course difficulty into account, giving higher points for advanced or honors classes.
Types of GPA Scales
GPA scales are not universal and can vary between institutions. The most common is the 4.0 scale, but some schools use a 5.0 or 6.0 scale, particularly for advanced courses. Weighted GPAs allow students to earn extra points for more challenging classes, making it possible to exceed a 4.0. There is also the percentage-based system, where grades are represented as percentages rather than points. Understanding the scale your school uses is critical to accurately interpreting academic performance.
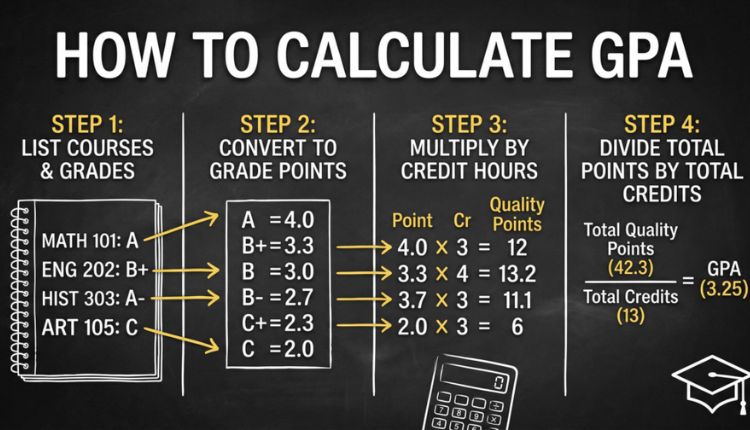
Calculating Your GPA
Calculating GPA involves converting letter grades to numerical values, multiplying by course credits, and then averaging. For example, if a student earns an A in a 3-credit course, a B in a 4-credit course, and a C in a 2-credit course, the GPA calculation would be: (4.0×3 + 3.0×4 + 2.0×2) ÷ (3+4+2). This calculation helps students track their academic performance and set goals for improvement. Many schools provide online GPA calculators to simplify this process, ensuring accuracy in assessment.
The Importance of the GPA Scale
The GPA scale is more than just a number; it is a reflection of a student’s dedication and consistency. A high GPA can enhance college applications, make students eligible for scholarships, and improve job prospects. Employers and graduate programs often look at GPA as an indicator of work ethic and commitment. Conversely, a low GPA may signal a need for academic improvement and strategic planning. Understanding how the GPA scale works allows students to make informed decisions about their academic journey.
Weighted vs. Unweighted GPA
A weighted GPA accounts for the difficulty of the courses taken. Advanced Placement (AP), International Baccalaureate (IB), or honors classes often carry extra points, which can boost the GPA above the standard 4.0. In contrast, an unweighted GPA treats all courses equally, regardless of difficulty. Both systems have their advantages, but it’s important for students to know which one their school emphasizes, especially when applying to colleges that consider GPA in their admissions process.
Common GPA Scale Variations Worldwide
While the 4.0 scale is common in the United States, other countries have different systems. For instance, some universities in Canada use a 4.3 scale, while others use letter grades only. In Europe, the 10-point scale is more common, and some Asian countries use percentage systems. Students aiming to study abroad should understand how their GPA converts to international scales to ensure accurate representation of their academic performance.
Tips to Improve Your GPA
Improving GPA requires consistent effort, time management, and strategic course selection. Students can focus on strengthening weaker subjects, participating actively in class, and seeking help when needed. Taking advanced courses can also improve a weighted GPA. Regularly monitoring grades and calculating GPA ensures that students stay on track toward achieving their academic goals. Building strong study habits and maintaining discipline can significantly impact GPA and future opportunities.
Conclusion
The GPA scale is a vital tool for measuring academic performance and guiding educational decisions. Understanding how it works, the types of scales, and strategies to improve it can help students achieve their full potential. Whether aiming for college admission, scholarships, or career advancement, maintaining a strong GPA is a key factor in long-term academic and professional success.